Q1: What is 3D printing in the context of advanced materials and technology? A1: 3D printing, within advanced materials and technology, is a precise manufacturing method where objects are built layer by layer, guided by digital models. It’s an essential technique for creating intricate and customized components.
Q2: How does the Laser Metal Deposition (LMD) process influence 3D printing? A2: LMD, a variant of 3D printing, explores parameters like laser power, powder flow, and density distribution to determine their impact on geometric properties, dilution, and microstructure in the creation of single and multiple layer workpieces.
Q3: What materials are typically used in advanced 3D printing processes like LMD? A3: In advanced 3D printing, materials such as cast iron and maraging steel are commonly used, often in various ratios to achieve specific properties and characteristics.
Q4: How does this impact advanced materials and technology development? A4: This informs the development of advanced materials and technology by refining the understanding of laser-based 3D printing processes, leading to improved precision and quality in manufacturing.
Q5: Can these insights be adapted to other 3D printing processes beyond LMD? A5: These insights contribute to the broader field of 3D printing. They can be applied to enhance the understanding of similar processes and their applications in various industries.
Q6: How can the precision achieved through 3D printing, especially in processes like LMD, benefit industries? A6: The precision offered by 3D printing, particularly in processes like Laser Metal Deposition (LMD), is invaluable for industries such as aerospace, healthcare, and automotive. It enables the creation of intricate and customized components with minimal material waste, reducing production costs and enhancing the performance and functionality of products.
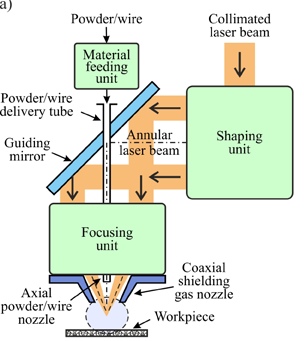
Scheme of the ALB, direct metal deposition head, by Govekar et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.08.099
